はじめに – 超短光パルスとは – / Introduction – What is Ultrashort Optical Pulses?
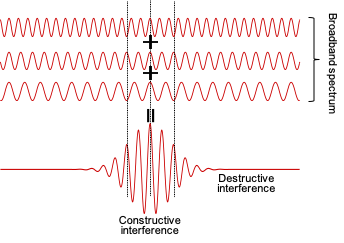
超短光パルスとは、10兆分の1秒程度の時間幅を有する非常に短い電磁波です。このような超短パルスは、多くの周波数(色)の光が位相をそろえて重ね合わされることで形成されます (Fig.1)。そのため、スペクトルが広いという特徴をもちます。また、光エネルギーが一瞬に込められているため、ピークパワーが高いという特徴ももちます。これらの特徴は、高速光通信、光による材料の加工、光計測などの応用において、有効に働くことが見出されています。また、基礎科学分野では、原子・分子・電子の高速な動きを観たり、コントロールしたりする能力をもっている点が魅力的です。
Ultrafast optical pulse is an electromagnetic wave that has a very short pulse width, broadband spectra, and high peak intensity (Fig.1). These features enable us to realize fast and reliable optical communication, laser processing, and various optical measurements. In addition to those applications, by using these technics we can access and control the dynamics of atoms, molecules, and electrons.
中赤外フェムト秒レーザーの開発 / Mid-Infrared Femtosecond Lasers
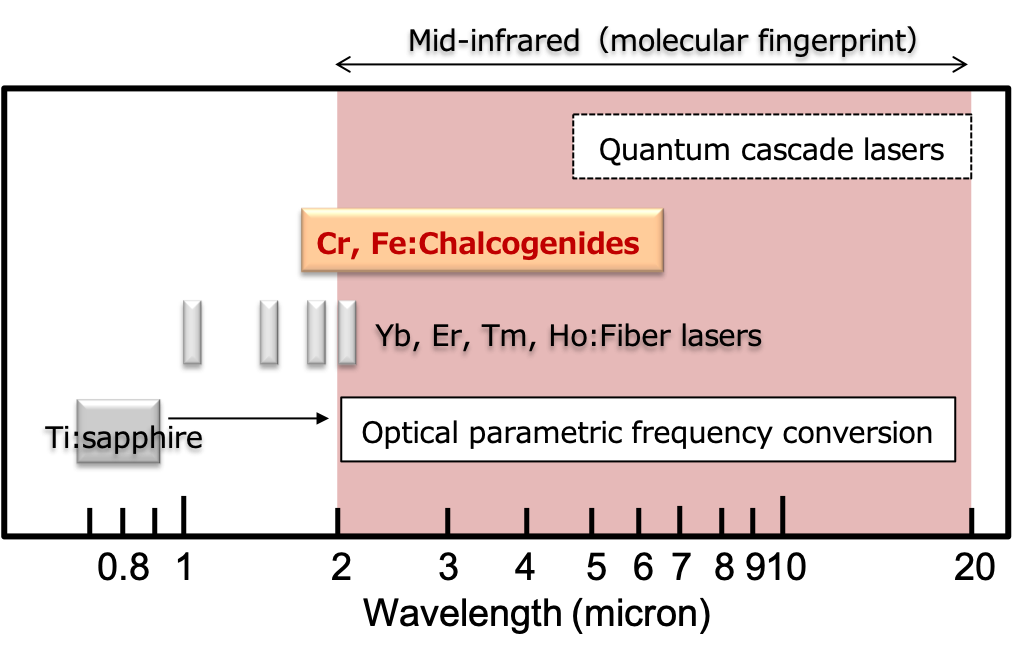
芦原研究室では、特に中赤外の波長領域に注目をしています。中赤外領域は古くから分子の指紋領域と呼ばれ、分子振動分光が盛んに行われてきました。これらの技術は環境・生体計測などに広く応用されています。他にも、ポリマー材料の光加工や長波長光通信で注目される波長域です。以上の背景から、中赤外領域の超短パルスレーザーは近年、非線形分子分光や高強度場非線形光学を中心とした様々な領域で需要が高まっています。
We are especially interested in the mid-infrared wavelength range. The mid-infrared region has been called the molecular fingerprint. Here, the vibrational absorption spectroscopy, which is applied to environmental and medical sensing, has been extensively investigated. Recently, mid-infrared femtosecond pulses are in high demand for nonlinear molecular spectroscopy and strong field nonlinear optics.
中赤外領域のフェムト秒パルスは、チタンサファイアレーザーなどから得られる近赤外域のフェムト秒パルスに対し、非線形光学効果を利用した下方周波数変換を用いて発生させる手法が一般的です (Fig.2)。
本研究室では、より簡単な構成で優れたエネルギー効率・ビーム品質を持つ中赤外フェムト秒光源システムの実現を目的として、中赤外領域で直接フェムト秒発振するレーザーの開発と応用に取り組んでいます。
特に、CrやFeイオンをII-IV族化合物にドープした物質は、中赤外領域に広い蛍光スペクトルを有し、レーザー媒質として優れた特性を持つため、中赤外領域の次世代レーザー媒質として注目を集めています。本研究室では、Cr:ZnS (Fig.3)を中心としたレーザー開発を行っています[1]。
Mid-infrared ultrafast light sources are prepared by applying frequency down-conversion techniques based on nonlinear optical effects to near-infrared femtosecond pulses obtained from Ti:Sapphire oscillator (Fig.2). In our laboratory, we are developing mid-infrared femtosecond lasers to realize better usability, energy extraction efficiency, and beam quality.
Cr, Fe doped II-VI materials show a broad fluorescent spectrum in the mid-infrared region and have superior properties for laser oscillation. Thus, they are now attracting a lot of attention. We are especially interested in Cr:ZnS (Fig.3) and succeeded in realizing femtosecond oscillation [1].
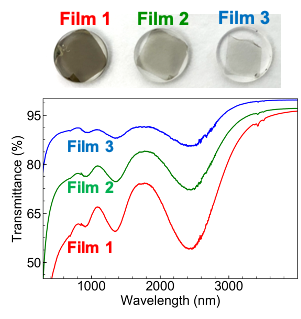
本研究では中赤外フェムト秒パルスの実現に、適切な直径を有する単層カーボンナノチューブ (SWCNT)を使用しています。本研究で使用するSWCNTはFig.4に示すように、中赤外域で共鳴するため、Cr:ZnSの発振波長で優れた可飽和吸収特性を示し [2]、フェムト秒パルス発振のセルフスタートという、実用上とても重要なレーザー特性を実現しています。
In this research, single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) with an appropriate diameter are utilized to realize mid-infrared femtosecond oscillation. As shown in Fig. 4, the SWCNT used in this study resonates in the mid-infrared region, so that it exhibits excellent saturable absorption characteristics at the oscillation wavelength of Cr:ZnS [2].

- D. Okazaki, H. Arai, A. Anisimov, E. I. Kauppinen, S. Chiashi, S. Maruyama, N. Saito, S. Ashihara, “Self-starting mode-locked Cr:ZnS laser using single-walled carbon nanotubes with resonant absorption at 2.4 μm,” Optics Letters, Vol.44, Issue.7, pp. 1750-1753 (2019).
- D. Okazaki, I. Morichika, H. Arai, E. I. Kauppinen, Q. Zhang, A. Anisimov, I. Varjos, S. Chiashi, S. Maruyama, S. Ashihara, “Ultrafast saturable absorption of large-diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes for passive mode-locking in the mid-infrared,” Optics Express vol.28, 14, pp. 19997-20006 (2020)

